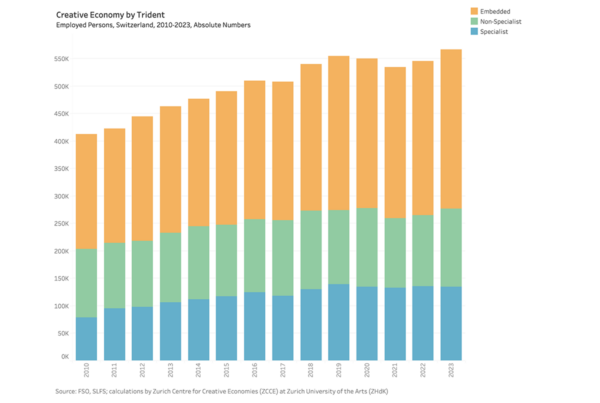
Following our Creative Economies Reports, we publish here regularly updates of the ZCCE Creative Economy Employment Estimates.
This statistical analysis approaches the creative economies from the perspective of professional activities and occupations.[1] It presents information on the creative economy workers – that is the employed persons working in the creative sector as well as persons working in a creative occupation outside the creative industries (“embedded”) – and their structural characteristics.
Mapping the Creative Economy Employment Switzerland
Our research allows us to analyse the size, trends, structural characteristics and geography of the creative economy employment in Switzerland.
Looking at the data, we can explore the number of creative workers according to socio-economic aspects such as sex, level of educational attainment, age, work-time percentage, contract form and income from employment as well as to working conditions such as multiple jobs, work location, evening/weekend work, night work, shift work or work on call.
The figures show the employment in the Swiss creative economy in the period 2021–2023 and the average of these three years.
Source: FSO, SLFS; own calculations Zurich Centre for Creative Economies (ZCCE) at ZHdK, www.creativeeconomies.com
Remark: In 2021, the Swiss Labour Force Survey (SLFS) used here has made a method change in the survey, from a telephone survey to an online questionnaire. For this reason, there is a method break: for part of the results greater caution should be exercised when comparing over time with the years prior to 2021. As part of the publication in July 2024, the data from the 1st quarter of 2021 to the 1st quarter of 2024 was revised retrospectively.
Overview
Between 2021 and 2023, about 549,000 people were employed in the Swiss creative economy on average. This represented 11% of the total workforce. About one half (267,000) were employed in the creative industries, while the other half (282,000) pursued a creative occupation outside the creative industries (“embedded”) in the wider creative economy.
If only those persons with a creative profession, i.e. creative occupation (417,000), are considered, around two thirds (282,000) earn their living outside the creative industries.
Employment is highest in the sub-sectors IT, software and computer services (181,000 employed persons), Advertising and marketing (123,000) and Architecture (99,000). These three sub-sectors account for over two thirds of all employed persons in the Swiss creative economy.
Methodology
Based on the classification for creative occupations and industries according to UK’s DCMS and Innovation Foundation Nesta,[2] we estimate the size of the Swiss creative economy employment and its three main components (specialist, non-specialist, and embedded employment) using the Swiss Labour Force Survey (SLFS).[3]
This approach rests on the assumption that creative occupations also exist outside the creative industries: «This methodology is based on the theoretical and empirical argument that the creative industries are ‘those industries that specialise in the employment of creative talent for commercial purposes’— that is, have unusually high proportions of their workforce employed in creative occupations (‘creative intensity’).»[4]
Creative economy employment is given by the sum of creative industries employment and all creative jobs in other industries (embedded jobs). The creative economy thus consists of three types of employees:
- Non–specialists (support): employed persons working in a creative industry, but who are not themselves employed in a creative occupation, for instance, a bookkeeper at a publishing company.
- Specialists: persons working in creative occupations in creative industries, for instance, a dancer in an ensemble or a journalist writing for a daily newspaper.
- Embedded: persons working in creative occupations outside the creative industries, for instance, a game designer working in financial services.
Further information in our Creative Economies Reports and in the Research Notes.
Notes
[1] See also our complementary analysis on creative industries enterprises with their businesses and employees.
[2] The Dynamic Mapping methodology, originally applied by Nesta to classify the creative economy, consists of three stages. First, a set of occupations is identified as creative. Second, the workforce intensity of these occupations is calculated for each industry. Third, based on the distribution of creative intensity across industries, a threshold intensity is identified, above which all industries are determined to be creative for measurement purposes, while those below the threshold are not. Finally, creative economy employment is estimated according to the Creative Trident approach.
See the classification of the creative occupations and industries according to UK’s DCMS and Innovation Foundation Nesta in the annexe.
[3] See Frédéric Martel, Christoph Weckerle, Roman Page, Grand Simon: «Sleeping Beauty – four research notes on the effects of the corona crisis». I-IV, ZCCE/ZHdK, 2020.
See Christoph Weckerle, Simon Grand, Frédéric Martel, Roman Page and Fabienne Schmuki, Entrepreneurial Strategies for a Positive Economy, 3rd Creative Economies Report Switzerland, Zürich 2018.
See Christoph Weckerle, Roman Page, Simon Grand: Von der Kreativwirtschaft zu den Creative Economies. Kreativwirtschaftsbericht Schweiz, Zürich 2016.
[4] Bakhshi Hasan, Hargreaves Ian, Mateos-Garcia Juan: A Manifesto for the Creative Economy. Nesta, London 2013.